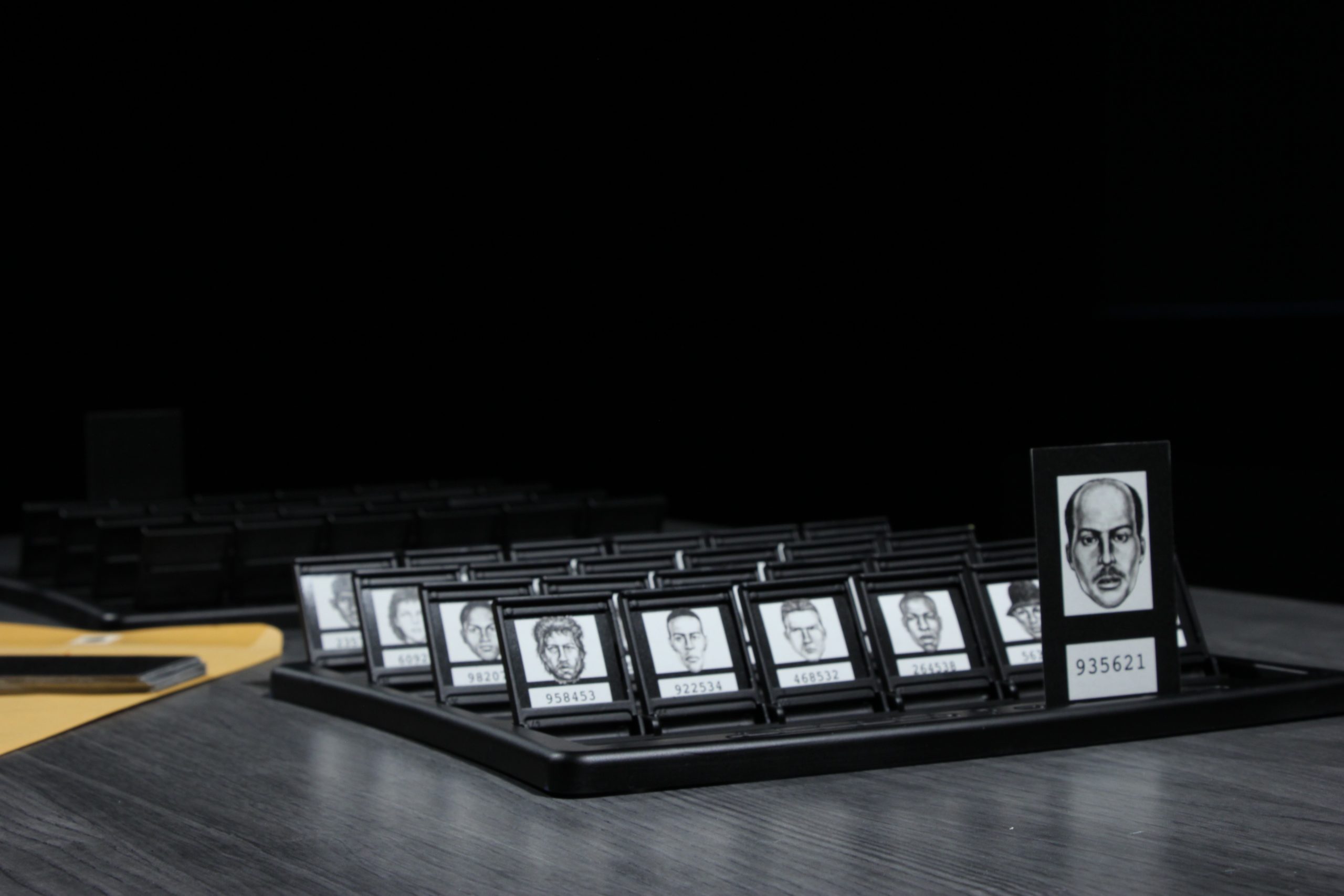
Guess who did the crime?: The Facial Composite Game
By Eliseo Ortiz (University of Colorado Boulder) In 1878, British psychologist Francis Galton wrote about the significance of photography in policing and incarcerating populations. Together with the famous jailer Edmund Du Cane, Galton investigated criminal behavior patterns by comparing the photographs of thousands of imprisoned inmates. Using eugenics as a guiding force to classify social behaviors, Galton developed several categories of criminals based solely on their physical features. Early on, this experiment consolidated a racist discourse fostered by the alleged truthfulness of photography. In the same way that the practice of phrenology called for measuring people’s skulls to determine mental traits and social behaviors, Galton superimposed series of photographs in order to find common physical patterns in criminals and concluded that “if criminals are found to have certain special features,” then “certain personal peculiarities distinguish those who commit certain classes of crime” as well.1 Galton inaugurated this approach back in 1878. Yet today, we are still experiencing the residue of a much more internalized racist discourse that justifies the persecution and systematic mass incarceration of …