Introduction / Issue 33: After Douglas Crimp
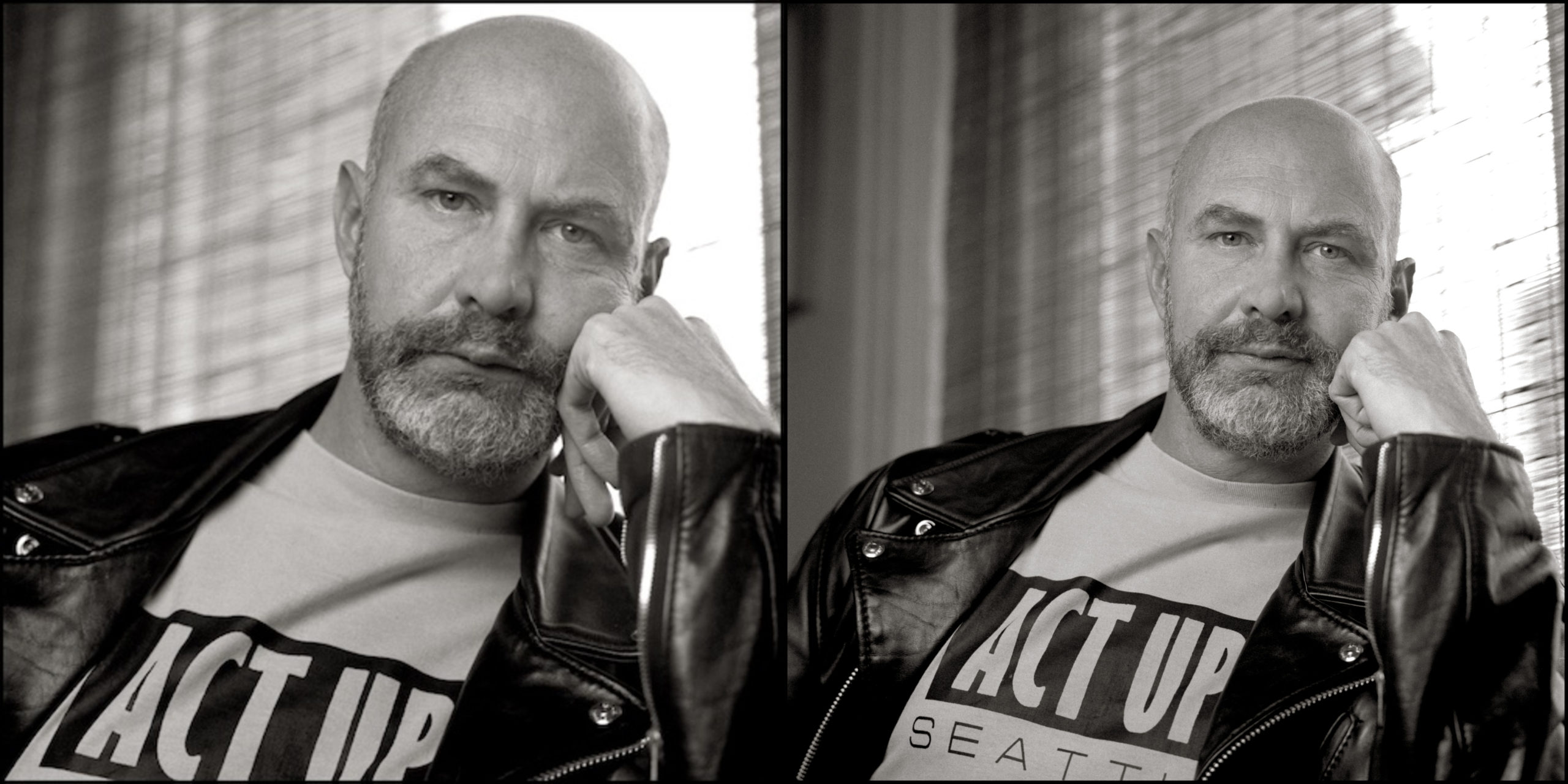
Click here for the Table of Contents by Peter Murphy Featured images: T.L. Litt, Douglas Crimp, New York, 1990. (L) and Douglas Crimp, New York, 1990. (R). Images courtesy of the artist. When it was time to decide the topic for Issue 33 of InVisible Culture, there was no question that it would be on anything other than Douglas Crimp (1944–2019). Douglas—someone who hardly needs an introduction, especially in the context of IVC—was an important figure for the journal and its affiliated graduate program in Visual and Cultural Studies. His pathbreaking essay “Getting the Warhol We Deserve,” for example, was published in our first issue. We would be remiss, however, to neglect to mention that Douglas was influential for an array of people and things: art history and criticism, queer theory and activism, gallery and museum exhibitions, and so many friends, students, and readers of his work. Given this vast network, our call for papers and artwork that engage with his legacy was a slight misnomer. There is no singular legacy to Douglas Crimp; instead, …